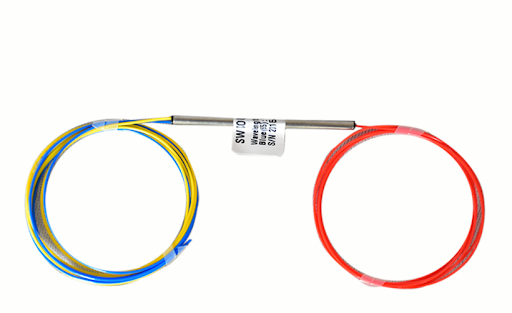
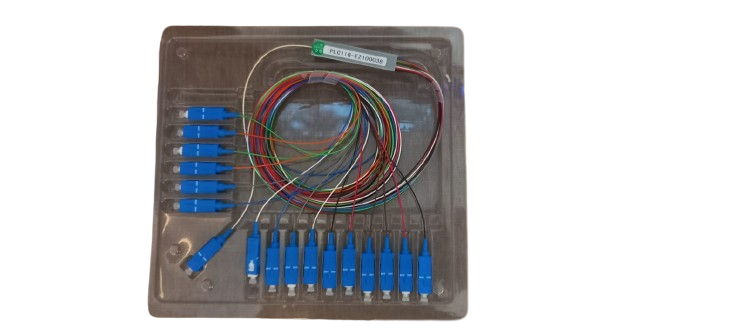
An optical fiber cable PLC splitter box cassette typically features: low insertion loss, uniform power splitting across all outputs, high reliability, compact size, excellent environmental stability, various package options, and compatibility with different fiber connector types; making it ideal for applications like FTTx networks, where a single optical signal needs to be distributed evenly to multiple users across a fiber optic network.
Key features of a PLC splitter box cassette:
- Passive operation: It is a passive device, meaning it does not require power to function, simply splitting the incoming optical signal without amplification.
- Customizable split ratios: Can be configured with different split ratios depending on the required power distribution across multiple outputs.
- Low PDL (Polarization Dependent Loss): Ensures minimal signal degradation based on the polarization of the light.
- High bandwidth: Supports a wide range of wavelengths, suitable for various communication applications.
- Compact design: Small footprint allows for easy integration into tight spaces within network equipment.
- Multiple connector types: Can be equipped with various fiber connector types like SC, LC, or FC to match existing infrastructure.
- Environmental stability: Designed to withstand temperature fluctuations and other environmental conditions.
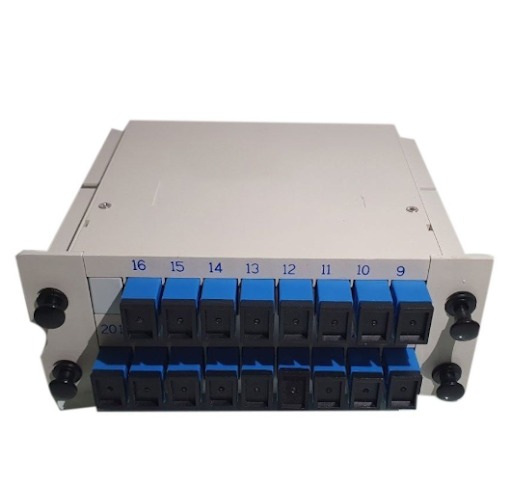
- Cassette format: Allows for easy insertion and removal from a rack-mountable chassis, simplifying installation and maintenance.
- Function: Splits an incoming optical signal from a single fiber into multiple output fibers with a predetermined split ratio, distributing the signal to various destinations.
- PLC technology: Utilizes Planar Lightwave Circuit technology, known for its high performance, low insertion loss, and good channel-to-channel uniformity.
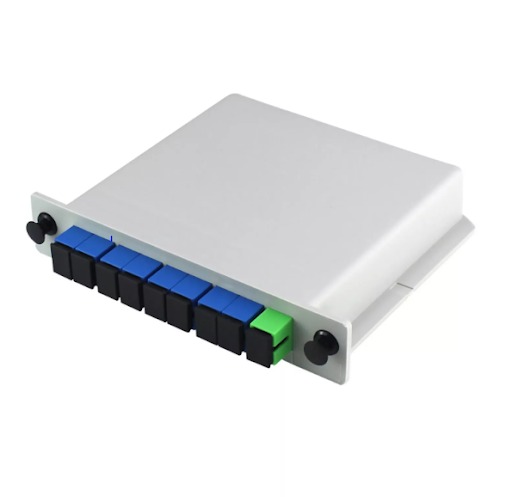
- Cassette design: A compact, modular design that fits neatly into a standard slot within a fiber distribution box, enabling easy installation and removal.
- Connectors: Typically equipped with standard fiber optic connectors like SC, LC, or FC, allowing for quick connection to other fiber optic cables.
- Applications: Widely used in FTTH networks, Passive Optical Networks (PON), and other scenarios where efficient signal distribution across multiple users is required
- FTTx networks (Fiber To The X): Distributing optical signals to multiple homes or businesses within a network
- Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPON): Efficiently splitting signals to multiple ONTs (Optical Network Terminals)
- CATV systems: Distributing cable TV signals to multiple subscribers
- LAN/WAN networks: Creating multiple data streams within a network infrastructure