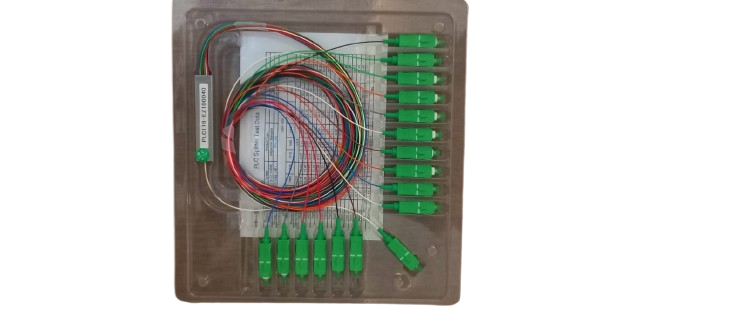
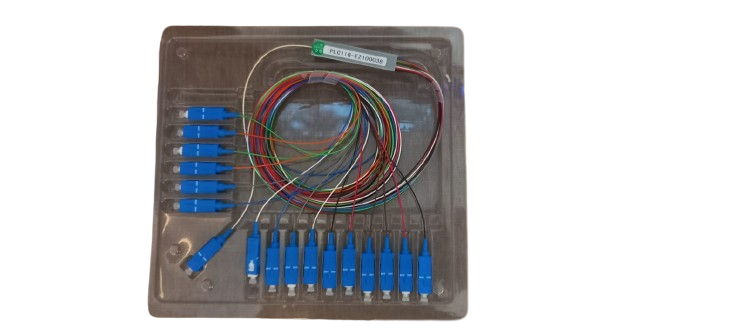
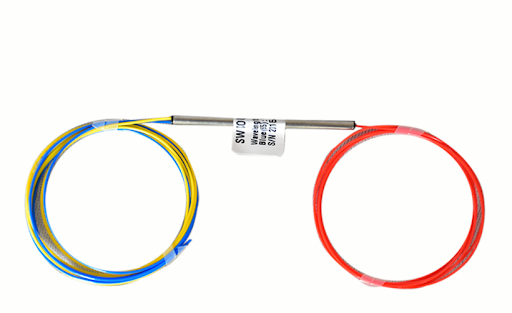
A PLC (Planar Lightwave Circuit) optical fiber cable splitter features: low insertion loss, excellent channel-to-channel uniformity, a wide operating wavelength range, compact design, high reliability and stability, and the ability to split an incoming optical signal into multiple equal outputs with minimal signal degradation; making it suitable for various fiber optic network applications where precise signal distribution is required.
Key features of a PLC splitter:
- Balanced power distribution: Evenly distributes the input optical signal across all output ports, ensuring each receiving device gets a consistent signal strength.
- Customizable split ratios: Can be manufactured with various split ratios (e.g., 1×2, 1×4, 1×8, etc.) to match specific network requirements.
- Wide operating wavelength: Operates across a broad range of wavelengths, allowing compatibility with different types of optical signals.
- Low polarization dependent loss (PDL): Minimizes signal loss based on the polarization of the light, ensuring consistent signal quality.
- Compact size: Offers a small footprint, ideal for dense network deployments.
- High stability: Resistant to environmental changes, providing reliable performance over time.
- Good channel-to-channel uniformity: Ensures consistent signal strength across all output ports.
Applications of PLC splitters:
- Fiber To The Home (FTTH): Distributing optical signals to multiple homes from a single fiber optic cable.
- Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPON): Enabling high-speed data transmission to numerous users.
- Data Center Networks: Splitting optical signals for efficient network infrastructure.
- Video Surveillance Systems: Distributing video signals to multiple monitoring points.
- Function: Splits an optical signal from a single input fiber into multiple output fibers with a predetermined power distribution ratio.
- Technology: Based on Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) technology, using semiconductor manufacturing techniques to create the waveguide structure on a chip.
- Applications: Primarily used in Passive Optical Networks (PON) like GPON, EPON, and BPON to connect the main distribution frame (MDF) to individual user terminals.
- Split Ratios: Can be configured with various split ratios depending on the network requirements, such as 1×2, 1×4, 1×8, 1×16, or even higher.
Benefits:
- High channel-to-channel uniformity, meaning each output port receives a similar amount of power.
- Low insertion loss, minimizing signal degradation
- Compact size, suitable for high-density applications